
Latest Cold, Flu & Cough News and Research
Can novel coronavirus affect pregnant women and their babies?
As the new coronavirus (COVID-19) becomes more of a concern for people around the world, fact and myth are increasingly being confused, particularly due to misinformation and unofficial advice being casually shared.
Knowing more about new infectious disease threat may not satisfy people
People who rate themselves as highly knowledgeable about a new infectious disease threat could also be more likely to believe they don't know enough, a new study suggests.
Dental shock: Six pulled teeth and one unexpected bill
The ache in three of Kathy McCracken's teeth started almost four years ago. It was hard for her to chew and swallow. She was sensitive to both hot and cold food.
CDC urges older people to stay at home amid coronavirus spread
The novel coronavirus is continuing to spread worldwide, with more than 113,000 cases and now more than 4,000 deaths. In the United States, health officials urge residents not to panic due to the viral infection’s low mortality rate. Still, they advise that older people are at the highest risk of coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
How does COVID-19 coronavirus compare to the 1918 Spanish flu?
The world has seen outbreaks, with some worst than others, but one thing is common, all these outbreaks result in loss of life and a global health crisis. One of the worst epidemics in the world was the 1918 Spanish flu. Now, the current coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak is being compared to the Spanish flu that ravaged the world more than a century ago.
Surging health care worker quarantines raise concerns as coronavirus spreads
As the U.S. battles to limit the spread of the highly contagious new coronavirus, the number of health care workers ordered to self-quarantine because of potential exposure to an infected patient is rising at an exponential pace.
Coronavirus spreads even without symptoms and how Hangzhou province contained virus spread
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is rapidly spreading across the globe, and containment measures have been implemented at many of the hotspots for the disease. Though isolation and quarantine measures are considered the best way to contain the virus, one new study suggests it might not be as effective as hoped.
Study looks at lung injury and vaping THC and vitamin E acetate
The US has witnessed a spate of patients presenting with acute lung injury associated with e-cigarettes or vaping product use. A new study published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine shows the pattern of the outbreak in California where recreational cannabis use is legal and which has among the maximum cases of the strange illness.
Scientists may have found a way to prevent coronavirus spread
Just like any other virus, the coronavirus needs a host to survive. Viruses enter the cells of the human body to cause disease by attaching to a specific receptor site on the host cell membrane. To do this, they attach to proteins in the capsid through glycoproteins found in the envelope of the virus.
Individual responsibility to prevent the spread of COVID-19 is equally vital as government action
How individuals respond to government advice on preventing the spread of COVID-19 will be at least as important, if not more important, than government action, according to a new commentary from researchers at the University of Oxford and Imperial College London in the UK, and Utrecht University and the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment in the Netherlands.
Focusing on healthcare quality as a business strategy
Despite two decades of effort - targeting care processes, outcomes, and most recently the value of care - progress has been slow in closing the gap between quality and cost in the US healthcare system.
TB bacteria produce fatty acid that triggers a pain-response cough to spread the disease
Tuberculosis is distinguished primarily by the persistent cough that serves to spread the disease. Stopping whatever triggers that cough could greatly reduce the transmission of the disease, which annually kills more than 1.3 million people worldwide.
Pence leaves out key details about health coverage of coronavirus testing
Amid ongoing concern about the new coronavirus, Vice President Mike Pence sought to assure Americans that their health insurance will cover the tests needed for diagnosis.
On front lines, first responders brace for coronavirus ― and their own protection
When first responders answered roughly 10 calls from a long-term care center in Kirkland, Washington, over the course of a week, they did not expect to become patients themselves.
The Pancreatic Cancer Collective awards additional funding of $16 million for new therapies
The Pancreatic Cancer Collective, the strategic partnership of Lustgarten Foundation and Stand Up To Cancer, has awarded additional funding of up to $16 million to four teams of top researchers as part of its "New Therapies Challenge Grants," the American Association for Cancer Research, Scientific Partner of SU2C, announced today.
Active censoring of coronavirus information 'enabled' by China for months
In keeping with China's often repressive policy towards news outlets and the dissemination of news and views that it doesn't want to be in the public domain, it is becoming apparent that Chinese social media WeChat and live-streaming app YY have long been editing what they display about the novel coronavirus illness.
Best practices shown to protect healthcare workers from COVID-19
In a new study published on March 5th, 2020, in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, researchers claim that the meticulous application of best practices for infection control does protect healthcare workers from the COVID-19 illness.
Coronavirus and currency notes – the connection
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended people to avoid using currency notes to prevent the spread of the COVID-19 virus or the novel coronavirus that has caused a global panic infecting over ninety-thousand individuals and killing over 3,000 up until now.
Tuberculosis bacteria facilitate their spread by producing a molecule that triggers cough
The bacteria that cause the deadly lung disease tuberculosis appear to facilitate their own spread by producing a molecule that triggers cough, a new study led by UTSW researchers shows.
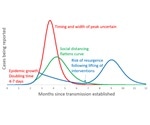
During a pandemic, states’ patchwork of crisis plans could mean uneven care
A possible coronavirus pandemic could overwhelm the nation's hospitals and force doctors into difficult decisions about how to allocate limited resources. Yet, experts say, only a handful of states have done the work necessary to prepare for such worst-case scenarios.





_977edb817b4c48c1a6724dcdef15fa53-150x125.jpg)



































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario