
Latest Coronavirus Disease COVID 19 News and Research
UV experts publish therapeutic exercise programs for people with physical ailments
Experts from the Faculty of Physical Therapy of Valencia University (UV) are warning that the physical exercise programs that have flooded the internet since the confinement due to the COVID-19 crisis can worsen the symptoms of people with physical ailments and lead to catastrophisation and pain chronification.
Non-invasive, low-cost ventilator developed for regions with limited means
Researchers from the Biophysics and Bioengineering Unit of the UB have created a non-invasive low-cost ventilator, to support patients with respiratory diseases in areas with limited means.
Sino Biological Partners with Nanommune Inc. to Develop and Market a Novel Coronavirus Multiplex Serological Assay
Sino Biological, Inc. today announced a co-development agreement with Nanommune Inc., an Irvine, California based biotechnology company specializing in the development and application of multiplex array technology.
‘It hurts our soul’: Nursing home workers struggle with thankless position
In the months before county health officials ordered the evacuation of COVID-19-plagued Magnolia Rehabilitation & Nursing Center, the facility's employees complained of bounced checks.
A new biosensor to quickly and reliably detect novel coronavirus
Jing Wang and his team at Empa and ETH Zurich usually work on measuring, analyzing and reducing airborne pollutants such as aerosols and artificially produced nanoparticles.
Study finds NCCN Guidelines for Patients listed among the most trustworthy online resources
A recently-published study from researchers in Australia and South Africa found the NCCN Guidelines for Patients to be among the most trustworthy resources for patients and caregivers seeking information online about prostate cancer.
The inside story of how the Bay Area got ahead of the COVID-19 crisis
Sunday was supposed to be a rare day off for Dr. Tomás Aragón after weeks of working around-the-clock.
San Francisco quick to fight COVID-19, slow to help homeless
San Francisco Mayor London Breed has won nationwide praise for taking drastic early measures against COVID-19 that seem to have spared San Francisco the catastrophic fate of New York and other cities.
A switch to Medicaid managed care worries some Illinois foster families
Rebecca and Bruce Austin in central Illinois have six kids — ranging in age from 4 to 22.
How Hong Kong reduced COVID-19 transmission
Amid the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, many countries across the globe have imposed lockdowns in an attempt to reduce the spread of the virus. Still, some countries have not opted for lockdowns, and community quarantines, and still are doing well. Hong Kong, for one, appears to have averted a major COVID-19 outbreak despite not imposing lockdown.
Australia may beat the novel coronavirus, modeling shows
Many countries are now in lockdown in an attempt to contain the spread of the novel coronavirus, now called the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus has sickened 2.47 million people worldwide, triggering many preventive measures. Now, it appears that preventive measures taken in Australia are containing the virus, according to a new modeling.
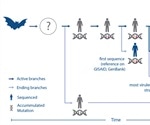
Scientists use genomics and bioinformatics to analyze blueprint of novel coronavirus
Australian researchers from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) have found a new way to decode the genome of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that causes COVID-19 disease. This approach could help in drug and vaccine development. Their work titled, "Supporting pandemic response using genomics and bioinformatics: a case study on the emergent SARS-CoV-2 outbreak," is published in the latest issue of the journal Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.
COVID-19 and immunodeficiency
COVID-19 disease, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a highly infectious disease. As of today, over 170,000 people worldwide have succumbed to the infection. Reports have shown that some comorbidities and illnesses raise the risk of getting infected and also influence the severity of the disease. Having a compromised immune system can also drastically raise the risk of getting COVID-19.
Does high COVID-19 viral load mean more risk of infection?
The risk of getting infected with COVID-19 disease is higher among healthcare workers who are in close contact with infected patients
Role of ACE/ARB inhibitors in the treatment of COVID-19
A new opinion piece published in the journal Circulation Research in April 2020 defends the use of antihypertensive drugs called ACE inhibitors and ARBs in patients with pandemic viral pneumonia called COVID-19.
University of Utah invests $1.3 million in multidisciplinary COVID-19 research projects
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the globe, University of Utah scientists are at the forefront of efforts to learn more about how to lasso the virus that causes it and understand its potential long-term social, economic, and psychological effects.
CSIRO researchers unveil new approach to understand evolving SARS-CoV-2 virus strains
Researchers from CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, have unveiled a new approach to analyzing the genetic codes - or the blueprint - of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
McKelvey engineers receive federal funding for rapid COVID-19 test
Engineers at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis have received federal funding for a rapid COVID-19 test using a newly developed technology.
ACE2 receptor expression by SARS-CoV-2 across different animal species
A new report published on the preprint server bioRxiv in April 2020 reports that several species of animals can be infected with relative ease by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that is the causative agent of the currently raging COVID-19 pandemic. This casts much light on the possible natural hosts and routes of transmission of this virus.
Mutations in novel coronavirus make it more dangerous
A new report published on the preprint server medRxiv in April 2020 reveals that the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 shows the presence of new mutations acquired within infected human cases, which significantly increase its ability to cause human disease.









_fe1b18bd588d47e2a72a8ed05bc03ae0-150x125.jpg)




































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario