
Latest Coronavirus Disease COVID 19 News and Research
Laboratory testing confirms effectiveness of BETADINE antiseptic products against SARS-CoV-2
Mundipharma today announced that laboratory testing at the Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore, has confirmed the effectiveness of its BETADINE antiseptic products against the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) which causes COVID-19 disease.
Charity warns of a catastrophic knock on effect for stroke research due to pandemic
Almost three quarters (74%) of stroke research projects funded by the Stroke Association have been suspended because of the coronavirus pandemic.
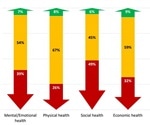
Colorado, like other states, trims health programs amid health crisis
As a teenager, Paulina Castle struggled for years with suicidal thoughts. When her mental health was at its most fragile, she would isolate herself, spending days in her room alone.
New clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of convalescent plasma to prevent COVID-19
There is only one approved, specific treatment for COVID-19, the illness caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, albeit with modest efficacy.
Researchers estimate global undercounting of COVID-19 cases
A new study by an international team of researchers and published on the preprint server medRxiv* in July 2020 describes a model to estimate the actual undercounting of COVID-19 cases and the global prevalence.
What people know and how they behave during COVID-19: Canadian perspective
Now, a new study by researchers in Canada and published on the preprint server medRxiv in July 2020 shows that national news is the primary source of information about the pandemic.
AI powered screening-test for COVID-19
A new study by researchers at the University of Oxford and Harvard University and published on the preprint server medRxiv in July 2020 reports the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to screen patients presenting or admitted to hospital for COVID-19. This could help triage patients in low-testing settings and help reduce infection risk.
As winter comes other viruses will compete with SARS-CoV-2 for susceptible hosts
A new study published on the preprint server medRxiv in July 2020 traces how COVID-19 became the predominant cause of respiratory infection in the period from early January until the present.
Study of 17 million patients pinpoints COVID-19 mortality risk factors
Now, an analysis of 17 million people in England, the most extensive study of its kind, sheds light on certain factors that can increase a person’s chances of dying from COVID-19, the disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Volunteers can now register for coronavirus disease vaccine trials
In an attempt to recruit many volunteers, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) has established a new clinical COVID-19 Prevention Trials Network (COVPN) that aims to enroll thousands of volunteers to test various investigational vaccines against the SARS-CoV-2 infection.
WHO confirms 'emerging evidence' of airborne coronavirus
Scientists from around the world wrote a letter to the World Health Organization (WHO), urging the agency to acknowledge that the novel coronavirus is airborne. More than 230 scientists presented evidence that people can catch the virus from droplets floating in the air.
Pigs and chickens not susceptible to SARS-CoV-2
A team of researchers in Germany aimed to investigate the susceptibility of potential animal hosts and the risk of zoonosis spill-over infections, which are illnesses transmitted to humans from animals. On the other hand, reverse zoonosis pertains to infections in humans that jump to animals.
Manifestations of COVID-19 in newborn babies
In a new study titled, “The clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 positive neonates,” Italian researchers led by Guiseppe De Bernado from Division of Pediatrics Neonatology and NICU, Ospedale Buon Consiglio Fatebenefratelli, Naples, explain the course of the infection among newborn babies.
Rat plague following COVID-19?
The COVID-19 pandemic led to the widespread closure of many business establishments, including eateries and restaurants. This kind of mass change in human behavior has historically led to changes in animal behavior as well. This is especially observed with respect to urban rat behavior.
Remdesivir potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cell cultures
The news about remdesivir, the investigational anti-viral drug that has shown early promise in the fight against COVID-19, keeps getting better.
Study outlines principles for delivering trauma-informed virtual care
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted a rapid expansion of telehealth use in the U.S. While articles have been published on telehealth and best practices for patient-centered communication during the crisis, none have focused on applying principles of trauma-informed care until now.
Novel antibody test for SARS-CoV-2
A team of researchers in the United States have developed highly specific and sensitive assays that could improve understanding of the antibody response in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and help to determine the effectiveness of vaccines.
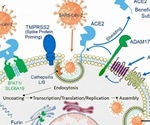
SARS-CoV-2 a dagger to the aging heart
Researchers in Europe have shown that genes involved in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection are expressed to a higher degree in older heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) than they are in younger cardiomyocytes.
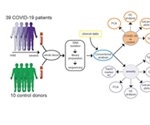
Use of whole blood transcriptomes may improve COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment
In a new paper published on the preprint server medRxiv*, a multinational group of researchers provide the first evidence for the use of whole blood transcriptomics to distinguish coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from other infections, and also to monitor and potentially predict disease outcomes.
Pasteurization of breast milk inactivates novel coronavirus
Pasteurizing breast milk using a common technique inactivates severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) making it safe for use, according to new research in CMAJ.





_441ce981e0344c3f83819cff83ecdab2-150x125.jpg)


_6a59efb441af4d85bc726db926b7c157-150x125.jpg)

































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario