
CORONAVIRUS DISEASE COVID 19 NEWS AND RESEARCH
Latest Coronavirus Disease COVID 19 News and Research
Oral hygiene and severity of COVID-19 – the connection
Their study titled, “Could there be a link between oral hygiene and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections?” was published in the latest issue of the journal British Dental Journal.
Herd immunity in the U.S. unlikely
The race to develop an effective vaccine against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is on, with many vaccine candidates entering the human trial phase. When a vaccine is developed and introduced into the population at scale, it triggers herd immunity, with many people immune to the infectious disease.
New swine flu strain with pandemic potential found in China
As the world grapples with a novel coronavirus pandemic, a new strain of swine flu that can trigger a pandemic has been reported.
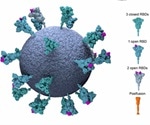
Striking CryoEM image of SARS-CoV-2
A new study by researchers from the UK and Germany and published on the preprint server bioRxiv in June 2020 reports the results of a detailed study of the S protein on the intact virus, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryoEM) and tomography. This could help understand the conformation of the S protein on the virion and how it interacts with neutralizing antibodies.
New approach holds incredible potential for developing new therapeutics
Nearly every drug that is, or has ever been, used was derived from nature -- harnessing compounds created by organisms over eons to fight diseases. But decades ago, biochemists postulated that it might be possible to design a new drug from scratch by linking up amino acids in precise ways.
Large-scale analysis of COVID-19 risk among different groups of UK hospital staff
Staff who shared a household with an infected person were at the greatest risk of infection, and those working in COVID-19-facing areas were also at an increased risk. Other groups that were identified as a high risk included Black and Asian individuals, porters, and cleaners.
Specific SARS-CoV-2 genetic elements found in different insect species
In a recent bioRxiv paper, researchers from Norway and the US demonstrate the presence of a highly conserved, mobile genetic element (thus far with unknown function) in genomes of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and a large number of insects – opening the door for hitherto unexplored treatment opportunities.
Potential new biomarker could improve COVID-19 diagnosis
Researchers at Montpellier University Hospital have discovered that an interferon-inducible receptor expressed on monocytes could be a useful biomarker for the rapid triaging of patients suspected to have severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Ghana's efforts to eliminate malaria at risk as economy improves
Ghana's efforts to eliminate malaria could be in jeopardy as its improved economy results in reduced external funding for fighting malaria, a study suggests.
SARS-CoV-2 can infect heart cells in a lab dish, study shows
A new study shows that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus), can infect heart cells in a lab dish, indicating it may be possible for heart cells in COVID-19 patients to be directly infected by the virus.
The biggest database for automated gait analysis
The database comprises information on the so-called "ground reaction force" which is the force between the foot and the ground that is generated during movement. It is an important standard parameter used in clinical practice and in research.
COVID-19 patients' blood can help identify people at greatest risk of severe illness
Doctors can examine COVID-19 patients' blood to identify those at greatest risk of severe illness and to pinpoint those most likely to need a ventilator, new research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine suggests.
Foldable tent-like device shields healthcare workers caring for COVID-19 patients
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore has invented a foldable tent-like device that serves as a physical shield to reduce the risk of exposure to pathogens for healthcare workers performing droplet and aerosol-generating procedures on COVID-19 patients.
Hospital executive charged in $1.4B rural hospital billing scheme
A Miami entrepreneur who led a rural hospital empire was charged in an indictment unsealed Monday in what federal prosecutors called a $1.4 billion fraudulent lab-billing scheme.
Workers filed more than 4,100 complaints about protective gear. Some still died.
COVID-19 cases were climbing at Michigan's McLaren Flint hospital. So Roger Liddell, 64, who procured supplies for the hospital, asked for an N95 respirator for his own protection, since his work brought him into the same room as COVID-positive patients.
Essential worker shoulders $1,840 pandemic debt due to COVID cost loophole
Carmen Quintero works an early shift as a supervisor at a 3M distribution warehouse that ships N95 masks to a nation under siege from the coronavirus. On March 23, she had developed a severe cough, and her voice, usually quick and enthusiastic, was barely a whisper.
Salk Institute expands research to find treatments and cures for COVID-19
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues across the globe, the Salk Institute joins in efforts to understand the fundamental science behind the novel coronavirus to pave the way to treatments and cures.
Newly identified molecules can help develop COVID-19 therapeutics
SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus causing the global COVID-19 pandemic, uses a protein called polymerase to replicate its genome inside infected human cells.
‘More than physical health’: Gym helps 91-year-old battle isolation
Most mornings, like clockwork, you could find Art Ballard pumping iron.
Spike protein and human ACE2 binding ability shows SARS-CoV-2 viral adaptation
A new study published on the preprint server bioRxiv in June 2020 reports some important findings that could shed light on this question. As the pandemic marches on, having claimed over 500,000 lives and caused well over 10 million infections to date, the task of defining and predicting factors that predispose to infectivity across species becomes ever more critical.
_0c37b19224e14c0d8e604e6017b58a53-150x125.jpg)




_36b1e52c2a0344b48878c3293e2c44dd-150x125.jpg)







_8869a5cade084a5d8bba7fe3bbf14964-150x125.jpg)
































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario