
Disease Burden of Influenza
Each year CDC estimates the burden of influenza in the U.S. CDC uses modeling to estimate the number of influenza illnesses, medical visits, flu-associated hospitalizations, and flu-associated deaths that occur in the U.S. in a given season. The methods used to calculate these estimates are described on CDC’s webpage, How CDC Estimates the Burden of Seasonal Influenza in the U.S.
CDC uses the estimates of the burden of influenza in the population and the impact of influenza vaccination to inform policy and communications related to influenza.
2017-2018 FLU SEASON BURDEN ESTIMATES
CDC calculates estimates of disease burden in the United States using surveillance data and modeling to adjust for sources of under-detection.

HOW CDC ESTIMATES THE BURDEN OF FLU
CDC uses modeling to estimate the number of influenza illnesses, medical visits, flu-associated hospitalizations, and flu-associated deaths that occur in the U.S. in a given season.
WHY CDC ESTIMATES THE BURDEN OF FLU
CDC uses the estimates of the burden of influenza in the population and the impact of influenza vaccination to inform policy and communications related to influenza.
Estimated Range of Annual Burden of Flu in the U.S. since 2010
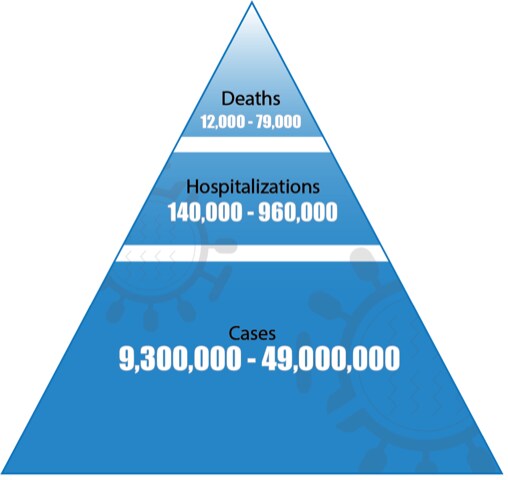
The burden of influenza disease in the United States can vary widely and is determined by a number of factors including the characteristics of circulating viruses, the timing of the season, how well the vaccine is working to protect against illness, and how many people got vaccinated. While the impact of flu varies, it places a substantial burden on the health of people in the United States each year.
CDC estimates that influenza has resulted in between 9.3 million – 49.0 million illnesses, between 140,000 – 960,000 hospitalizations and between 12,000 – 79,000 deaths annually since 2010.
| Symptomatic Illnesses | Medical Visits | Hospitalizations | Deaths | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | Estimate | 95% Cr I | Estimate | 95% Cr I | Estimate | 95% Cr I | Estimate | 95% Cr I |
| 2010-2011 | 21,000,000 | (20,000,000 – 25,000,000) | 10,000,000 | (9,300,000 – 12,000,000) | 290,000 | (270,000 – 350,000) | 37,000 | (32,000 – 51,000) |
| 2011-2012 | 9,300,000 | (8,700,000 – 12,000,000) | 4,300,000 | (4,000,000 – 5,600,000) | 140,000 | (130,000 – 190,000) | 12,000 | (11,000 – 23,000) |
| 2012-2013 | 34,000,000 | (32,000,000 – 38,000,000) | 16,000,000 | (15,000,000 – 18,000,000) | 570,000 | (530,000 – 680,000) | 43,000 | (37,000 – 57,000) |
| 2013-2014 | 30,000,000 | (28,000,000 – 33,000,000) | 13,000,000 | (12,000,000 – 15,000,000) | 350,000 | (320,000 – 390,000) | 38,000 | (33,000 – 50,000) |
| 2014-2015 | 30,000,000 | (29,000,000 – 33,000,000) | 14,000,000 | (13,000,000 – 16,000,000) | 590,000 | (540,000 – 680,000) | 51,000 | (44,000 – 64,000) |
| 2015-2016 * | 25,000,000 | (24,000,000 – 28,000,000) | 12,000,000 | (11,000,000 – 13,000,000) | 310,000 | (290,000 – 340,000) | 25,000 | (21,000 – 31,000) |
| 2016-2017 * | 30,000,000 | (28,000,000 – 32,000,000) | 14,000,000 | (13,000,000 – 16,000,000) | 580,000 | (520,000 – 660,000) | 51,000 | (44,000 – 64,000) |
| 2017-2018 * | 49,000,000 | (46,000,000 – 53,000,000) | 23,000,000 | (21,000,000 – 25,000,000) | 960,000 | (870,000 – 1,100,000) | 79,000 | (69,000 – 99,000) |
* Estimates from the 2015-2016, 2016-2017, and 2017-2018 seasons are preliminary and may change as data are finalized.
































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario