
High Cholesterol and Stroke Risk
A stroke is a cardiovascular disease that can greatly affect the health status and quality of life of affected individuals. High cholesterol is a single condition that can lead to many complications, such as being a risk factor for stroke.
Blood Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is found in the fats or lipids in the blood. The body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, but too much of it can lead to various diseases, such as heart disease and stroke.
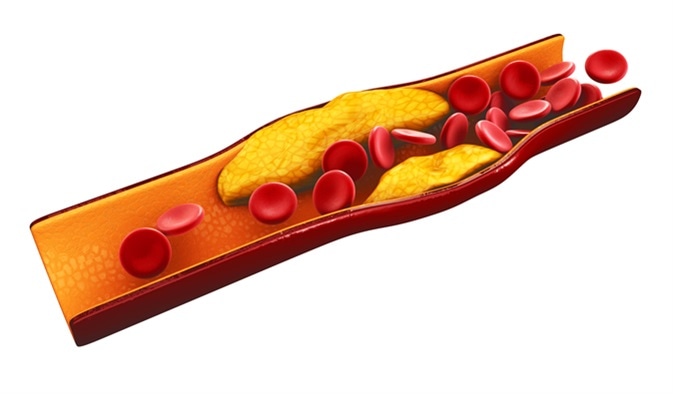
3d Illustration of blood cells with plaque buildup of cholesterol. Image Credit: Victor Josan / Shutterstock
High cholesterol levels can lead to the development of fatty deposits in the blood vessels. When these deposits accumulate, it makes it hard for blood to flow through the arteries. When the heart does not receive as much oxygen as it needs, a heart attack may result. When the brain does not receive oxygen, it can lead to a stroke.
High cholesterol is usually caused by lifestyle factors, such as faulty diet. It can also be inherited from the parents.
Lipoproteins carry cholesterol in the blood – low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Low-density lipoprotein is also called “bad” cholesterol because it is the main culprit in cholesterol build-up. On the other hand, high-density lipoprotein is also called “good” cholesterol because it helps keep cholesterol from building up in the blood vessels.
High Cholesterol Risk Factors
There are many factors that may increase one’s risk for high blood cholesterol levels.
- Obesity - Obesity, or a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more, puts a person at risk of having high cholesterol.
- Unhealthy eating habits - Consuming high amounts of saturated fats or trans fats can boost the levels of low-density lipoproteins in the blood.
- Lack of physical activity - Spending a lot of time sitting or lying down, without exercising, has been associated with lower levels of HDL and increased levels of LDL.
- Smoking - Smoking can lower the amounts of HDL, particularly in women. It also increases the levels of LDL in the blood.
- Genetics - People who have parents or siblings with high cholesterol are more likely to have the condition too.
- Diabetes - People with high blood sugar levels are at a greater risk of developing high cholesterol, with low levels of high-density lipoprotein (LDL), and high levels of bad cholesterol or LDL.
What is a Stroke?
Each year, more than 795,000 Americans suffer a stroke, a brain attack, or cerebrovascular accident. A stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, limiting the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the nerve cells. Another way a stroke occurs is when a blood vessel breaks, stopping blood flow to an area in the brain, shutting off the oxygen supply. As a result, the part of the brain affected can cause problems in functions such as thinking, talking, breathing, and walking.
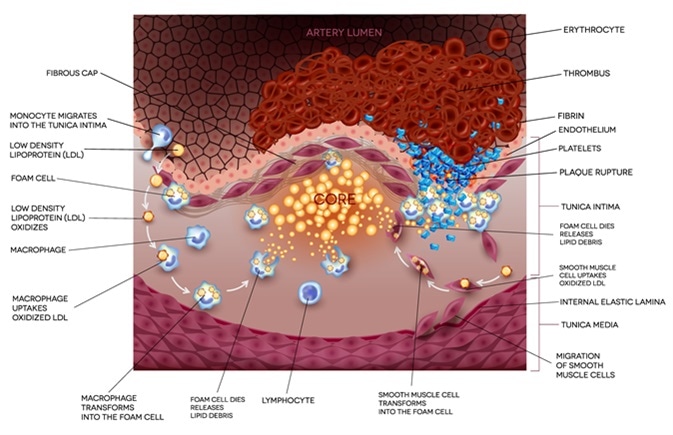
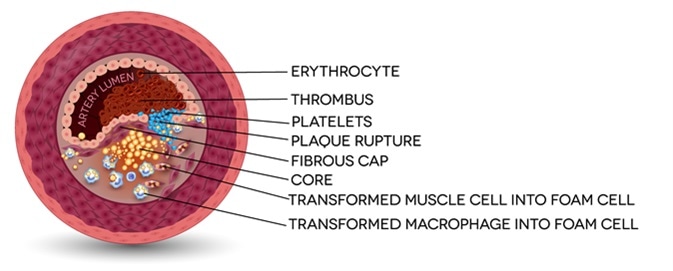
Ischemic stroke in the cerebral artery. Unstable plaque formation and thrombus. Image Credit: Tefi / Shutterstock
Stroke Risk Factors
There are numerous factors that can increase one’s risk of stroke. These include:
- High blood pressure - High blood pressure or hypertension makes a person four to six times more likely to have a stroke. High blood pressure is identified as a too high pressure of blood within the arteries, weakening the arterial wall. When the wall is too weak, it can rupture and break. A stroke happens when the ruptured blood vessel is in the brain.
- High cholesterol - Too high cholesterol levels in the blood may cause a stroke or a heart attack. Cholesterol may lead to the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, reducing the supply of blood and oxygen to the brain. When a part of the brain does not receive the needed oxygen, it may lead to problems with talking, walking, breathing, and movements.
- Diabetes - High blood glucose can damage the arteries in the long run. Diabetes may also increase the risk of hypertension and the formation of blood clots.
- Obesity - Being obese or overweight may increase one’s risk of having a stroke since it can increase the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Heart disease - Various heart conditions may increase the risk of a stroke because most of them are caused by disease processes that affect all the blood vessels in the body, including those in the brain. Some of these diseases include atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, heart valve disease, and heart failure.
High cholesterol and Stroke
High cholesterol may increase the risk of stroke by boosting the risk of vascular disease, which is a risk factor for stroke. When there is a plaque or fatty deposit build-up in the arteries due to high cholesterol, the blood flow to the brain can be blocked, reducing the amount of oxygen reaching the brain cells.
Sources:
Further Reading
Last Updated: Oct 26, 2018


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario