Hereditas
The evolution of transcriptional repressors in the Notch signaling pathway: a computational analysis
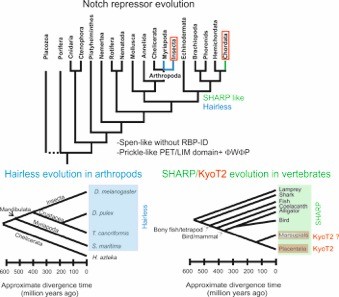
The Notch signaling pathway is highly conserved in eukaryotes. Notch repressors, however, are only known from arthropods and vertebrates (Drosophila: Hairless, vertebrates: SHARP/MINT and KyoT2). Database searches revealed homologues of Hairless only after the Chelicerata-Mandibulata radiation, SHARP only in vertebrates, and KyoT2 with a ΦWΦP interacting motif only in placental mammals. However, the data provide a hypothesis on the evolution of KyoT2 from Prickle-like ancestors. These Prickle-like ancestors contain a novel, putative CSL interacting motif. If it were confirmed by experiments, this work has uncovered a novel, very ancestral CSL interactor found in the entire animal kingdom.

































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario