
What is Chromosome 4?
Chromosome 4 is the fourth largest of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 4 is made up of over 186 million base pairs, the building blocks of DNA which are tightly packed and super coiled to from the DNA helix. Chromosome 4 represents around 6% to 6.5% of the DNA in the human genome.
Chromosone 4 contains approximately 1600 genes and approximately 190 million base pairs, of which ~95% have been determined. Image Credit: NIH
Genetic research is focused on identifying the genes on our chromosomes and estimates suggest that chromosome 4 contains around 1000 to 1100 genes. Gene mutations on chromosome 4 have been linked to genetic disorders and identified in several types of cancer.
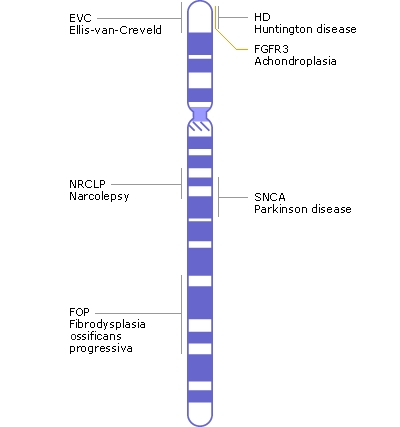
Examples of conditions associated with gene mutations on chromosome 4 include neurological and neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and narcolepsy. Chromosome 4 also plays a role in other disorders such as the connective tissue disorder fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva and a form of dwarfism called achondroplasia.
Some of the genes that are located on chromosome 4 include:
- ANK2 (codes for neuronal ankyrin 2)
- CRMP1 (codes for Collapsin response mediator protein 1)
- CXCL1 to 13 (codes for the chemokines, Platelet factor-4, interleukin 8 etc.)
- EVC and EVC2 (mutations lead to Ellis van Creveld syndrome and Ellis van Creveld syndrome 2)
- FGFR3 (codes for fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 absence of which leads to achondroplasia, bladder cancer, dwarfism)
- FGFRL1 (codes for fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1)
- Complement Factor I, HTT (codes for huntington protein)
- MMAA (codes for methylmalonic aciduria)
- PHOX2B (codes for homeodomain transcription factor)
- PKD2 (mutations of which leads to autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 2),
- QDPR (codes for quinoid dihydropteridine reductase)
- SNCA (codes for synuclein, alpha)
- UCHL1 (codes for ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1)
- WFS1 (codes for Wolfram syndrome 1)
- FGF2 (codes for fibroblast growth factor 2)
- KDR (Kinase insert domain receptor) etc.
Sources
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 15, 2019

































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario