
Latest Coronavirus Disease COVID 19 News and Research
Ineffective immune responses may be responsible for COVID-19 mortality rates in men and the elderly
News-Medical speaks to Dr. Nicole Lieberman about her latest research that discovered delayed immune responses may affect COVID-19 mortality rates.
S-pseudotyped VLPs offer promising COVID-19 vaccine platform
A new study published on the preprint server bioRxiv* in September 2020 reports on a Moloney murine leukemia virus (MLV) platform that produces VLPs expressing the important spike antigen of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Key China COVID-19 study produced results that influenced subsequent research on coronavirus
Early in the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, a small study in China produced results that influenced subsequent research on the virus.
Study invalidates Ebselen and other broad-spectrum SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors
Other novel compounds with Mpro inhibitory activity have also been claimed to have antiviral activity. These include ebselen, disulfiram, tideglusib, carmofur, shikonin, and PX-12. A new research paper discusses the role of these molecules as potential Mpro inhibitors in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A new framework to improve global sustainability
From loaning pandas to welcoming tourists to hike to sacred monuments, to regulating the sale of wild animals for meat, policies across the world seek to forge clear paths to sustainability.
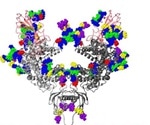
Study sheds new light on the mechanism of COVID-19 infection
The spike protein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus can adopt at least ten distinct structural states, when in contact with the human virus receptor ACE2, according to research from the Francis Crick Institute published in Nature today.
Engineered, high-affinity ACE2 receptors neutralize SARS-CoV-2
In a study published in the preprint server bioRxiv, researchers from the Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine and Osaka University Japan, discuss how they engineered ACE2 to enhance its affinity to RBD in human cells.
Animal data supports efficacy of baricitinib vs SARS-COV-2
The high burden of disease caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has led to much research on effective ways to mitigate the health, social, and economic impact of the spread of the infection. A recent study published on the preprint server bioRxiv* in September 2020 reports on the characteristics of the drug baricitinib when used as monotherapy to treat severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
T cells on the front line of COVID-19 response
In the new study, published in the journal Cell, the team has found that the uncoordinated responses produced by the immune system, especially in people who are more than 65 years old, maybe the reason why older adults are more at risk.
Mayo Clinic's tracking tool features latest COVID-19 data, expert guidance
The number of COVID-19 cases is surging in some regions and retreating in others, making consistent, reliable information and personalized guidance on the pandemic more important than ever.
Safer UVC light effectively kills SARS-CoV-2
A study conducted by Hiroshima University researchers found that using Ultraviolet C light with a wavelength of 222 nanometers which is safer to use around humans effectively kills SARS-CoV-2 -- the first research in the world to prove its efficacy against the virus that causes COVID-19.
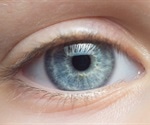
Wearing eyeglasses protects against SARS-CoV-2
A team of scientists from China suggests that people who wear eyeglasses for more than 8 hours a day may be less susceptible to infection by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. The study is published recently in the journal JAMA Ophthalmology.
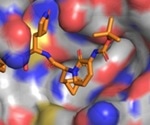
New drug candidate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication
Researchers at Stanford University and Utah State University have developed a novel inhibitor of the coronavirus main protease (Mpro) that effectively suppresses the viral replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Flexibility of glycosylated membrane-bound ACE2 suggests mechanical energy source in opening of SARS-CoV-2 spike
Angiotensin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2, Cell, Coronavirus, Enzyme, Glycoprotein, Neck, Protein, Receptor, Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Syndrome, Virus, SARS-CoV-2, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19,
Could pineapples be a new weapon against COVID-19?
Results of a recent research endeavor from the United States indicate that bromelain or bromelain rich pineapple stem may be utilized as an antiviral agent against coronavirus disease (COVID-19), but also for potential future coronavirus outbreaks. This exciting paper is currently available on the bioRxiv preprint server.
KHN’s ‘What the Health?’: It’s scandal week
President Donald Trump finally released his promised executive order aimed at bringing down drug costs.
LOX-1-immature neutrophils may help identify COVID-19 patients at risk of thrombosis complication
To predict severe outcome in COVID-19 patients, innate immune cellular signals are analyzed, identifying two novel neutrophil subsets: LOX-1- and CD123-expressing CD10-CD64+. Thromboembolic events correlated with high LOX-1 immature neutrophils – a potential prognostic signature.
COVID-19 could be diagnosed using stroke scans
New research from King's College London has found that COVID-19 may be diagnosed on the same emergency scans intended to diagnose stroke.
Students’ mass migration back to college gets a failing grade
Who thought it would be a good idea to move thousands of teenagers and young adults across the country to college campuses, where, unencumbered by parental supervision, many college kids did what college kids do?
Black women turn to midwives to avoid COVID and ‘feel cared for’
From the moment she learned she was pregnant late last year, TaNefer Camara knew she didn't want to have her baby in a hospital bed.
_d88610d49a3941ca9b704100868a8595-150x125.jpg)




_7c0819d131494e608f32f51e348883db-150x125.jpg)




































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario