
Topical Probiotics for Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory disease of the skin in which the normal barrier function of the skin is disrupted, so that immune function is impaired and susceptibility to infection with common bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus is increased.
Staphylococcus aureus grow on Mannitol salt agar. Image Credit: Pattikky / Shutterstock
This invasion by pathogenic microbes in turn leads to a disturbance in the numbers and relative proportions of various microbial species that live as commensal organisms on the skin, causing cutaneous dysbiosis.
Why is eczema treatment so urgent?
Atopic dermatitis is a common skin disorder, affecting about one in five children in developed nations. Moreover, it can profoundly disturb the individual’s quality of life and healthcare expenditures. Furthermore, atopic dermatitis is associated with development of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food allergies. Children will often not cooperate with the multiple applications and oral medications that make up its treatment at present, and either way, their quality of life is decreased. More effective biologics are now available but the cost is still steep, putting it out of reach in many places.
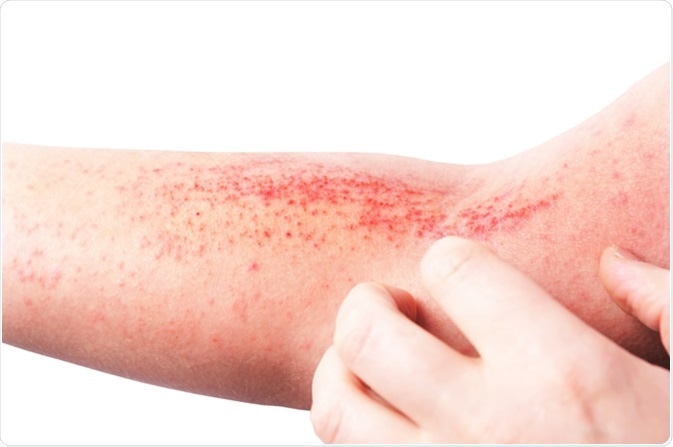
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema. Image Credit: LIAL / Shutterstock
Its incidence is shooting up in more developed nations, but most affected people will experience a marked reduction in symptoms around the time of puberty.
The chronic risks do not stop here, however, for the long duration during which the skin fails to provide a proper barrier to the invasion of foreign microbes and the removal of moisture takes its toll in the subsequent development of a hypersensitive skin which reacts to many other antigens.

































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario