
Signs and Risk Factors for Eye Disease
Eye diseases are widespread around the globe. According to the World Health Organization, the most important three eye diseases or conditions that are a potential threat to the global population are diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration. One more vital reason for visual harm is refractive errors. Some of the important reasons for vision loss or low vision are age, healthcare, gender, genetic problems and the prevalence of family history.
Signs and Risk Factors
Various eye diseases are mentioned below along with their symptoms/signs and risk factors.
Glaucoma
When the pressure in the eye increases due to the fluid inside, it damages the eye’s optic nerve. This condition is termed as glaucoma. Two types of glaucoma are—the primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and angle closure glaucoma (ACG).
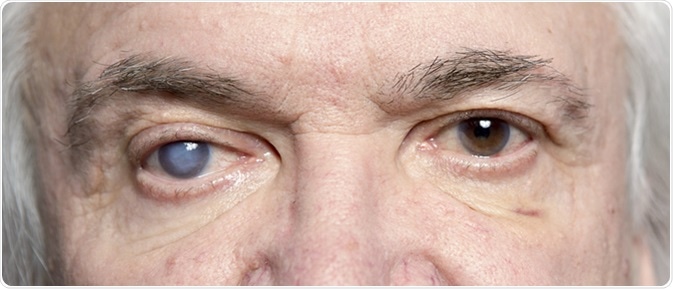
Glaucoma - Image Credit: Sergei Primakov / Shutterstock
Signs
Signs of POAG are gradual loss of peripheral vision in both the eyes; the advanced stage is marked by losing the passageway vision completely. Signs of ACG are severe pain, vomiting sickness and queasiness, the abrupt inception of visual trouble, frequently in low brightness, unclear vision, halos in the region of lights, and reddening in both the eyes.
Risk Factors
POAG risk factors are age and genetic makeup. Smoking, aging, alcohol consumption, eye infections, poor nutrition, UV damage, Injuries and accidents, hypertension, ocular hypertension, diabetes, and heredity are the various factors associated with glaucoma.
Cataract
If the lens of the human eye is shadowed and prevents a clear vision, then it is termed as cataract.
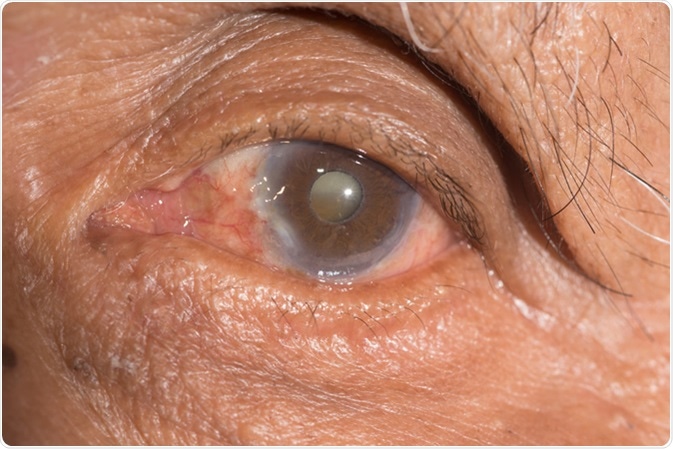
Close up of cataract - Image Credit: ARZTSAMUI / Shutterstock
Signs
Symptoms of cataract are a shadowy vision, faded colors, glaring, the problem in night vision, and dual vision.
Risk Factors
People with a diabetic family history have a high-risk factor for developing cataracts. Other factors include aging, eye infections, UV damage, injuries and accidents, high myopia, ocular hypertension, steroid medicines, and heredity.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication resulting from diabetes. As the progressive damage occurs in the vascular cells of the retina (which is responsible for good vision), it results in diabetic retinopathy.
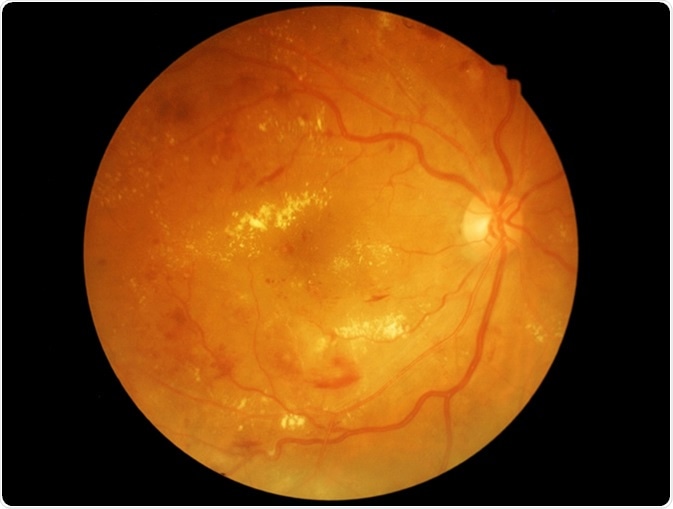
Diabetic Retinopathy - Image Credit: memorisz / Shutterstock
Signs
No symptoms occur during the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, however, loss of vision marks the advanced stage. Other signs include unclear vision, straining the eyes to see, and headaches related to eyestrain.
Risk Factors
Presence of diabetes, high blood pressure, glycemia levels, pregnancy, serum lipids levels, and sometimes genetic and nutritional factors.
Refractive Errors
Myopia and hyperopia with or without astigmatism (unclear vision at almost all levels), and presbyopia are the refractive errors found.
Signs
Symptoms of refractive errors are dual vision, circle of halos when seeing brightly ignited lights, squinting of the eyes due to eyestrain, headache related to the strain of the eyes, and vagueness.
Risk Factors
Adult people are affected by refractive errors, specifically presbyopia or hyperopia. Myopia can affect both children and adults. If parents have one or two of the refractive errors, it is more likely the children will be affected.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Macular degeneration occurs because of aging and results in damage to the vital and sharp vision of the eyes.
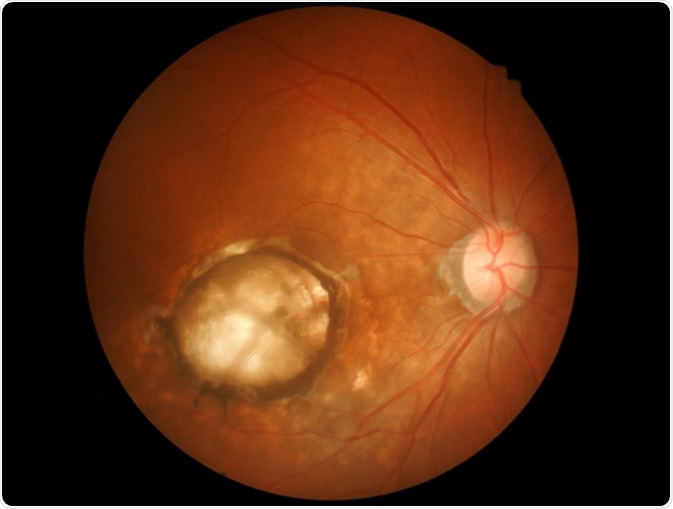
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) - Image Credit: memorisz / Shutterstock
Signs
Symptoms are an unclear vision, straight shapes appear bent/curved, etc.
Risk Factors
Tobacco use, genetic factors, hypertension, heart diseases, smoking, high hyperopia, heredity, and impartial or not so balanced diet are the risk factors related to AMD.
Corneal Inflammations and Ulcers
Corneal infections and ulcers are mainly caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or a parasite. Conjunctivitis, keratitis, and dry eye are some of the diseases related to this.
Signs
Some of the symptoms are eye pain, light sensitivity, reduced or glared vision, redness/inflammation, headache, vomiting sickness, weariness.
Risk Factors
Injuries, inflammations, poor nutrition, and UV damage.
Photophobia
Photophobia is the condition in which when light enters the eye, it hurts and results in discomfort. It is not a disease, but a symptom of many other problems.
Signs
Signs of photophobia include severe pain in the eye and sensitivity when exposed to any kind of light sources (sunlight/fluorescent light/incandescent light). Other symptoms are needed for squinting or closing the eyes, headache and nausea. Symptoms worsen with bright light.
Risk Factors
Severe infection of the eyes, burning sensation in the eyes, scratch in the cornea, infection due to wearing contact lenses excessively, meningitis, migraine headaches, and medications like atropine, trifluridine, and scopolamine.
Blepharitis
It is an eyelid-related disease wherein the eyelids are infected, scratchy, and become reddened. This can occur due to dandruff fragments that get deposited at the bottom of the eyelashes or other microbial infections.
Signs
Symptoms include reddened eyelids, dandruff debris that can be found at the base of the eyelids, burning/itching sensation, and puffiness of the eyelids.
Risk Factors
Bacterial overgrowth, people having a complaint of dandruff in the scalp, dry skin, diabetes, poor cleanliness, and people sensitive to chemical make-up items may have blepharitis in common.
Sources
- http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs282/en/
- http://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/
- http://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index1.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/visionhealth/basics/ced/
- http://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index8.html
- http://www.brightfocus.org/glaucoma/symptoms-and-signs
- www.health.gov.au/.../ap3.pdf
- nei.nih.gov/.../Diabetic-Retinopathy-What-You-Should-Know-508.pdf
- https://medlineplus.gov/maculardegeneration.html
- https://nei.nih.gov/health/cornealdisease/
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001004.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003041.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001619.htm
Further Reading
Last Updated: Aug 23, 2018

































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario