
Latest Coronavirus Disease COVID 19 News and Research
Study defines new starting points for therapy and vaccine research on coronavirus
The SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infects lung cells and is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The viral spike protein mediates entry of the virus into host cells and harbors an unusual activation sequence.
Newly identified antibody prevents SARS-CoV-2 virus from infecting cultured cells
Researchers at Utrecht University, Erasmus Medical Center and Harbour BioMed (HBM) today reported that they have identified a fully human monoclonal antibody that prevents the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) virus from infecting cultured cells.
As lawmakers reconvene, not everyone agrees on COVID-only agenda
California lawmakers return to the Capitol this week to begin what they describe as necessary but painful negotiations to keep the state running and redirect dwindling funds to the costly coronavirus pandemic.
COVID-plagued California nursing homes often had problems in past
When Jorge Newbery finally got through to his 95-year-old mother, Jennifer, on a video call April 18, she could barely talk or move and her eyes couldn't focus.
As COVID-19 lurks, families are locked out of nursing homes. Is it safe inside?
Families are beset by fear and anxiety as COVID-19 makes inroads at nursing homes across the country, threatening the lives of vulnerable older adults.
Study reveals variable sites in novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Understanding the varying aggressiveness of SARS-CoV-2 may provide valuable data to trace its spread across populations. In the study, published on the preprint server BioRxiv, the researchers traced amino acid variants that possess high frequency in Europe, particularly in Italy, one of the hardest-hit countries.
Eco-friendly technique could enable hospitals to produce hydrogen peroxide
A team of researchers has developed a portable, more environmentally friendly method to produce hydrogen peroxide. It could enable hospitals to make their own supply of the disinfectant on demand and at lower cost.
Scientists develop CRISPR-based test for SARS-CoV-2
Now, a team of scientists at the University of California Santa Barbara has developed a low-cost, rapid, and high-tech test that can detect SARS-CoV-2 effectively. They have developed a CRISPR-based test that is sensitive and effective as traditional tests.
New project launched to reduce COVID-19 infection among emergency room workers
Dr. David Talan, professor of emergency medicine and medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the UCLA medical school will lead the trial with co-principal investigator Dr. Nicholas Mohr, vice chair for research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at the University of Iowa.
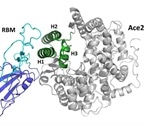
SARS-CoV-2 receptor ‘mimic' could prevent COVID-19
Researchers from Italy have developed an exciting new peptide drug that could potentially prevent the coronavirus from infecting people’s cells. The paper, published on the preprint server bioRxiv* in April 2020, describes a small molecule that can bind to and block the attachment site on the virus spike protein, preventing its entry into the host cell.
Impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy and breastfed infants
Pregnant women are among those at high risk of developing COVID-19, as confirmed in Wuhan early in the pandemic. A new study from Portugal published on the preprint server medRxiv in May 2020 analyses the data on the impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy and disease outcomes, using published cases of pregnant women diagnosed with the illness.
Kudos Pro: A communications platform for coronavirus-related research
Kudos, the award-winning service for accelerating research impact, has today announced that it is opening up its leading research communications platform - Kudos Pro - to the global academic community, with complimentary access for 60 days.
Research detects a more dangerous SARS-CoV-2 mutation
A new study published on the preprint server bioRxiv in May 2020 reports the setting up of a system to help track new mutations in the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that is behind the current COVID-19 pandemic. This will help analyze mutations to find and track the spread of those that are most likely to increase the pathogenicity of the virus, either by making it easier to transmit or by enhancing its resistance to treatment.
Australia's lockdown measures halt COVID-19 for now
A new study from the University of Melbourne finds that measures taken by the Australian public and government have effectively contained the spread of COVID-19 in Australia for the present. The paper is published on the preprint server medRxiv in May 2020.
Rapid affordable viral testing kits for low-resource settings
A new paper published on the preprint server bioRxiv* in April 2020 reports a low-cost, sensitive and rapid RT-PCR testing kit for the detection of COVID-19. If validated, this could provide an enormous boost to diagnostic testing in low-resource regions of the world.
Scripps professor receives Research Program Award for advancing RNA-targeting medicines
In recognition of his high-impact work advancing the field of RNA-targeting medicines, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded Scripps Research Chemistry Professor Matthew Disney, PhD, a prestigious Research Program Award, to aid Disney's development of treatments for incurable diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, ALS and frontotemporal dementia.
No rise in COVID-19 cases as Denmark eases lockdown
Outside of Asia, Denmark became the first nation to ease the forced social distancing norms or lockdown. Last week on Thursday, the officials declared that since the removal of the lockdown, there had been no rise in the number of COVID-19 cases. Their easing of the lockdown rules has been gradual, say the officials, and this process began in mid-April. There have been 9,721 reported cases and 484 deaths due to COVID-19 to date. The number of cases has also declined since 7th April.
Hydroxychloroquine combined with azithromycin and abnormal heart rhythms in COVID-19 patients
A new study shows that the initially lauded combination of drugs against COVID-19 - Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine combined with azithromycin, could lead to abnormal and life-threatening heart rhythms. In patients hospitalized with the novel coronavirus infection or SARS CoV-2, this combination can lead to prolonged QT interval as can be detected on ECG.
Study reveals antiviral properties of glycosaminoglycans against SARS-CoV-2
Glycosaminoglycans can inhibit cell invasion by acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and other coronaviruses, which supports the utilization of such therapeutics in the fight against coronavirus disease (COVID-19) – reports a new study available on the preprint server bioRxiv.
Low molecular weight heparins inhibit SARS-CoV-2 cell invasion
A recent paper available on the preprint server bioRxiv* reports preliminary data on the ability of low molecular weight heparins to interact with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), elicit structural changes in its key proteins and subsequently halt cell invasion.










_6182ff9574f34cd0908e110cdcde20be-150x125.jpg)
































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario