Featured Review: The roles of tumor-derived exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical implications
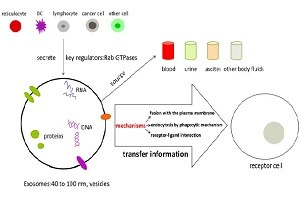 Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of lung cancer cases, and is one of the leading causes of cancer death in men and women worldwide due to diagnosis in the advanced stage, rapid metastasis, and recurrence. New methods are needed to develop real-time monitoring of drug efficacy and drug resistance, such as new molecular markers for more effective early detection and prediction of prognosis.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of lung cancer cases, and is one of the leading causes of cancer death in men and women worldwide due to diagnosis in the advanced stage, rapid metastasis, and recurrence. New methods are needed to develop real-time monitoring of drug efficacy and drug resistance, such as new molecular markers for more effective early detection and prediction of prognosis. Exosomes are nano-sized extracellular vesicles and play an important role in the development of lung cancer by controlling a wide range of pathways. Tumor-derived exosomes are of great significance for guiding the targeted therapy of NSCLC and exosomes themselves can be a target for treatment. In this review, Zheng et al. describe the potential roles of tumor-derived exosomes and their clinical significance in NSCLC.
Click here to access the full article.
Click here to access all of the reviews published to date in Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.


































No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario